1. Explain and discuss practical and theoretical aspects of Human-Computer Interaction.
Thinking creatively
Personas
Interface Usability for Old People
More Info on Use Cases
Cognitive Walkthrough and Task Analysis
Questionnaires
2. Apply HCI Principles to Practical Problems
Personas
Persona: Major Singh
Persona: Tony
Persona: Maureen
Brainstorming
Personas and age group brainstorm
Technology Brainstorm
Prototype meeting for ShopNav
Paper Design and Interface of Device
Idea: Shopping Advisor
Idea: Bringing High-Tec to the Old Age
Idea: New Generation of Laptop!!
Idea: Modify The Brain!
Idea: Speed Granny!
Idea: The Shopping Trip
Paper Design and Interface of Device
Questionnaires
ShopNav Questionnaire
Questionnaire Results: Shopping Habits of the Elde...
Prototyping
Prototype: Device Touchscreen Interface
Prototype meeting for ShopNav
Prototype: Hardware Device
Prototype: Trolley Design
Prototype: Supermarket RFID Service
Prototype: ShopNav Store Card
Criticisms
Final Idea: The Ultimate Shopping Experience
Modifications to our final Idea
Summary of Evaluation Techniques
Task Analysis and Scenarios
Scenarios: Purchasing Goods with Tony
Scenarios: Shopping for Goods with Major Singh
Task Analysis
Walkthroughs and Heuristic Evaluation
Cognitive Walkthrough by Major Singh
Cognitive Walkthough by Maureen
Cognitive Walkthrough by Tony
Heuristic Evaluation
Summary of Evaluation Techniques
3. Participate in Analysis and Design Work in HCI
Personas
Persona: Major Singh
Persona: Tony
Persona: Maureen
Brainstorming
Personas and age group brainstorm
Technology Brainstorm
Prototype meeting for ShopNav
Paper Design and Interface of Device
Idea: Shopping Advisor
Idea: Bringing High-Tec to the Old Age
Idea: New Generation of Laptop!!
Idea: Modify The Brain!
Idea: Speed Granny!
Idea: The Shopping Trip Paper Design and Interface of Device
Questionnaires
ShopNav Questionnaire
Questionnaire Results: Shopping Habits of the Elde...
Prototyping
Prototype: Device Touchscreen Interface
Prototype meeting for ShopNav
Prototype: Hardware Device
Prototype: Trolley Design
Prototype: Supermarket RFID Service
Prototype: ShopNav Store Card
Criticisms
Final Idea: The Ultimate Shopping Experience
Modifications to our final Idea
Summary of Evaluation Techniques
Task Analysis and Scenarios
Scenarios: Purchasing Goods with Tony
Scenarios: Shopping for Goods with Major Singh
Task Analysis
Walkthroughs and Heuristic Evaluation
Cognitive Walkthrough by Major Singh
Cognitive Walkthough by Maureen
Cognitive Walkthrough by Tony
Heuristic Evaluation
Summary of Evaluation Techniques
Testing and Evaluation
Final Prototype: ShopNav
Evaluation
4. Demonstrate appreciation of the research literature in one subfield of HCI.
(Jagdeep Biling)
HCI Extended Report: Blogging & wikis - a new form...
Friday, 30 March 2007
Evaluation
Future Releases
After further evaluating our final prototype we decided to re visit the local community centre, Onnely House in Harborne. We asked for their opinions on the product and we have taken their feedback to establish the following improvements to our product:
When taking the final prototype to the community centre, the elderly people gave great feedback on the product. They were very impressed with certain features such as the navigation tool which reduced the amount of working, the health monitoring system which took into concern the specific health problems and the need for no queuing because transactions were taken via the RFID readers.
The team is pleased in how we implemented the user design process and watched our idea blossom in the last 10 weeks.
After further evaluating our final prototype we decided to re visit the local community centre, Onnely House in Harborne. We asked for their opinions on the product and we have taken their feedback to establish the following improvements to our product:
- A My Pharmacy feature – this feature will call previous prescriptions, allow re-fill orders and notifies a user when the order is ready
- A map of the supermarket that will list products by location, and will also indemnify where the user is currently located
- A My Deli feature which allows the user to place orders and be notified when a order is ready
- Special store offers can be targeted to specific users
- Voice feedback system that navigates the user around the supermarket
- Provide users with an instructions leaflet
- Ensure the user interface remains simple, as the amount of functions in the system increase because this will inevitably augment complexity
- A menu hierarchy which tells the user where they are – similar to the windows menu hierarchy
- Include a receipt printing feature on the device when the user purchases their shopping via the RFID sensors
Overall Evaluation
We initially outlined a problem area regarding supermarket shopping for elderly people. Our objective was to reduce the amount of problems involved with shopping at a supermarket.When taking the final prototype to the community centre, the elderly people gave great feedback on the product. They were very impressed with certain features such as the navigation tool which reduced the amount of working, the health monitoring system which took into concern the specific health problems and the need for no queuing because transactions were taken via the RFID readers.
The team is pleased in how we implemented the user design process and watched our idea blossom in the last 10 weeks.
Thursday, 29 March 2007
HCI Extended Report: Blogging & wikis - a new form of interaction?
Author: Jagdeep Biling
ID: 328274
Web Logs and Wikis have grown in popularity in the past few years; they have been fixated into the mainstream providing a range of useful services. They are both user based websites, where users can add, edit and delete information content with the simplest of interaction for mass collaboration, which represent the online intersection of people and time (Werbach 2001). [1] The users range from political consultants, news services to the average Joe, used as a communication entity and a social paradigm. Interaction between people has evolved through time, and the Internet has opened a spectrum of different avenues for human interaction, are Blogs and Wikis the next revolutionary form of interaction entities?
It has been widely documented that Blogs and Wikis are the most explosive outbreak in the information world since the Internet itself. [2] Some argue that its just a fad, and will lose its appeal, but many sites have gained great popularity that provide blogging functionality of putting up user personal information and then connecting to networks all over the world, some of these include Facebook and MSN Spaces.
One of the fascinations is that something can be globally distributed via the click of a button, and then can be accessed real time anywhere in the world. With the Internet and technology offering a range of multimedia types to be posted, allows users to share experiences in real-time. An example of this is when the Tsunami occurred in Asia a couple of years ago, many people recorded the videos, which were posted on the internet soon after. [3] Something that traditional media services would need time to procure information and video footage before people can be informed over the world. [4] Deuze outlines how Blogs are becoming a new form of journalism that illustrates stories and experiences, which also allow readers to comment. [5]
Blogs and Wikis also allows for wanna-be writers to post their material, so Blogs and Wikis act as a distribution channel. A lot of the material does tend to be below publishing standards, but there is some outstanding material.
As human beings, we are social mammals and the need to socially interact is a must. Blogs and Wikis provide a process in which users can socially interact and share. This could be in the form of writing about day-to-day life to release frustrations to having a debate on a certain subject. There is also the ego gratification angle, where users feel the need to be the centre of attention, so they enjoy people reading information about them and commenting. [6]
However, there are certain controversies surrounding Blogs and Wikis, accuracy and validity of certain information can be brought into contention, with many traditional media services have a reputation to uphold about the credibility of their stories, and also legal considerations and the threat of being sued gives the user a sense of validity. There is also a range of legal liabilities to consider, such as users releasing confidential information about companies they work for and about other people, which can have serious consequences. Also putting up copyrighted media, such as music videos, a great example is Youtube where no one could be sued or stopped posting copyrighted material, now Google have purchased it they have had to remove much of the content, but it remains difficult to stop users from posting.
A new dawn of social interaction is among us, being able to communicate with anyone, anywhere in the world. Blogs allow for real-time discussions over the internet. Wikis become larger and more reliable through time and users adding and confirming information creating an ever-increasing database of information that can be accessed in 1 common area.
[1] Branum, J. 2001. The Blogging Phenomenon: An Overview and Theoretical Consideration, http://www.ajy.net/jmb/blogphenomenon.htm
[2] Pinto, J. 2005. Blog Phenonmenon all Around. http://www.isa.org/Content/ContentGroups/News/20051/September29/Pintos_Point__Blog_phenomenon_all_around.htm
[3] Pruitt, C. 2005. The Blogging Phenomenon: Who? How? Why?. http://www.digitaldivide.net/articles/view.php?ArticleID=86
[4]Kidman, A. 2005. The Blog Phenomenon. http://technology.ninemsn.com.au/article.aspx?id=28229
[5] Branum, J. 2001. The Blogging Phenomenon: An Overview and Theoretical Consideration. http://www.ajy.net/jmb/blogphenomenon.htm
[6] Dvorak, J. 2002. The Blog Phenomenon. http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,1895,81500,00.asp, TITLE
ID: 328274
Web Logs and Wikis have grown in popularity in the past few years; they have been fixated into the mainstream providing a range of useful services. They are both user based websites, where users can add, edit and delete information content with the simplest of interaction for mass collaboration, which represent the online intersection of people and time (Werbach 2001). [1] The users range from political consultants, news services to the average Joe, used as a communication entity and a social paradigm. Interaction between people has evolved through time, and the Internet has opened a spectrum of different avenues for human interaction, are Blogs and Wikis the next revolutionary form of interaction entities?
It has been widely documented that Blogs and Wikis are the most explosive outbreak in the information world since the Internet itself. [2] Some argue that its just a fad, and will lose its appeal, but many sites have gained great popularity that provide blogging functionality of putting up user personal information and then connecting to networks all over the world, some of these include Facebook and MSN Spaces.
One of the fascinations is that something can be globally distributed via the click of a button, and then can be accessed real time anywhere in the world. With the Internet and technology offering a range of multimedia types to be posted, allows users to share experiences in real-time. An example of this is when the Tsunami occurred in Asia a couple of years ago, many people recorded the videos, which were posted on the internet soon after. [3] Something that traditional media services would need time to procure information and video footage before people can be informed over the world. [4] Deuze outlines how Blogs are becoming a new form of journalism that illustrates stories and experiences, which also allow readers to comment. [5]
Blogs and Wikis also allows for wanna-be writers to post their material, so Blogs and Wikis act as a distribution channel. A lot of the material does tend to be below publishing standards, but there is some outstanding material.
As human beings, we are social mammals and the need to socially interact is a must. Blogs and Wikis provide a process in which users can socially interact and share. This could be in the form of writing about day-to-day life to release frustrations to having a debate on a certain subject. There is also the ego gratification angle, where users feel the need to be the centre of attention, so they enjoy people reading information about them and commenting. [6]
However, there are certain controversies surrounding Blogs and Wikis, accuracy and validity of certain information can be brought into contention, with many traditional media services have a reputation to uphold about the credibility of their stories, and also legal considerations and the threat of being sued gives the user a sense of validity. There is also a range of legal liabilities to consider, such as users releasing confidential information about companies they work for and about other people, which can have serious consequences. Also putting up copyrighted media, such as music videos, a great example is Youtube where no one could be sued or stopped posting copyrighted material, now Google have purchased it they have had to remove much of the content, but it remains difficult to stop users from posting.
A new dawn of social interaction is among us, being able to communicate with anyone, anywhere in the world. Blogs allow for real-time discussions over the internet. Wikis become larger and more reliable through time and users adding and confirming information creating an ever-increasing database of information that can be accessed in 1 common area.
[1] Branum, J. 2001. The Blogging Phenomenon: An Overview and Theoretical Consideration, http://www.ajy.net/jmb/blogphenomenon.htm
[2] Pinto, J. 2005. Blog Phenonmenon all Around. http://www.isa.org/Content/ContentGroups/News/20051/September29/Pintos_Point__Blog_phenomenon_all_around.htm
[3] Pruitt, C. 2005. The Blogging Phenomenon: Who? How? Why?. http://www.digitaldivide.net/articles/view.php?ArticleID=86
[4]Kidman, A. 2005. The Blog Phenomenon. http://technology.ninemsn.com.au/article.aspx?id=28229
[5] Branum, J. 2001. The Blogging Phenomenon: An Overview and Theoretical Consideration. http://www.ajy.net/jmb/blogphenomenon.htm
[6] Dvorak, J. 2002. The Blog Phenomenon. http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,1895,81500,00.asp, TITLE
Sunday, 25 March 2007
Final Prototype: ShopNav
After analysing the results from the evaluation techniques, several changes have been made to the prototype.
This blog entry will outline the final prototypes user interface design, menu navigation, device hardware design and the trolley design
This blog entry will outline the final prototypes user interface design, menu navigation, device hardware design and the trolley design
Wednesday, 14 March 2007
Summary of Evaluation Techniques
After carrying out our task analysis, cognitive walk through and heuristic evaluation we identified several weakness in our proto-type. These weak points will now be listed:
From the Task Analysis:
- If the user forgets their PIN number
- If the user can't find the desired product on search
- If the user does not follow the on screen navigation instructions
- What happens if the user is refused credit
- Conflict between the cashier and the user between prices
From the Cognitive Walk-through:
- Language Support
- Annoying recommendations keep repeating itself
- An on screen guide showing how to enter the card
- Intelligent search
- Display photos of the items
- Display where in the shopping process she is - what's next to be found on the shopping list
- Show an animation when an item is being detected in the trolley
- Allows the user to set the fat, sugar and salt content intake
- Shows all the offers that are applicable to the user
From the Heuristics Evaluation
- The system does not tell the user what part of the shopping process they are at, for instance does not tell the user that they are logging in
- The measurements are in metric, but the old people understand imperial
- Change font size control
- Change 'Begin Route' to 'Start Shopping' a phrase they are more familiar with
- Too much Red is used
- Help screens need to available in necessary places
From the Task Analysis:
- If the user forgets their PIN number
- If the user can't find the desired product on search
- If the user does not follow the on screen navigation instructions
- What happens if the user is refused credit
- Conflict between the cashier and the user between prices
From the Cognitive Walk-through:
- Language Support
- Annoying recommendations keep repeating itself
- An on screen guide showing how to enter the card
- Intelligent search
- Display photos of the items
- Display where in the shopping process she is - what's next to be found on the shopping list
- Show an animation when an item is being detected in the trolley
- Allows the user to set the fat, sugar and salt content intake
- Shows all the offers that are applicable to the user
From the Heuristics Evaluation
- The system does not tell the user what part of the shopping process they are at, for instance does not tell the user that they are logging in
- The measurements are in metric, but the old people understand imperial
- Change font size control
- Change 'Begin Route' to 'Start Shopping' a phrase they are more familiar with
- Too much Red is used
- Help screens need to available in necessary places
Heuristic Evaluation
To make this as least painful as possible I'm going to write down the Neilsens Heurisitics and underneath each heading try and make a comment on HCI point about our software.
Visibility of system status.
The system should always keep users informed about what is going on, through appropriate feedback within reasonable time.
The ShopNav unfortunately fails terribly at Visibility of System Status. The Log on Screen does not mention that is actually logging the person on, but just to insert the store card and then to enter a password. When first logged in the user does not know that they need to search for an item before they can start ShopNav. When the ShopNav is giving directions it does not state what item it is taking the user to.
Match between system and the real world.
The system should speak the users' language, with words, phrases and concepts familiar to the user, rather than system-oriented terms. Follow real-world conventions, making information appear in a natural and logical order.
When directing the user, the ShopNav displays in metric, old people would prefer imperial measurements.
The word 'Begin Route' could cause confusion, but renaming the button to 'Start Shopping' would clarify to old people that start shopping is exactly that.
The text can be too small sometimes for the old people with poor eye sight to read, need a font size changer feature.
User control and freedom.
Users often choose system functions by mistake and will need a clearly marked "emergency exit" to leave the unwanted state without having to go through an extended dialogue. Support undo and redo.
The system does allow the user to remove items so if anything does get entered incorrectly it can be removed easily.
The system however does not allow the user to log in because there is no keyboard to enter the pin number!
There is a lot of use of red which is not good because for old people most of them could experience colour blindness which would leave them not seeing much on the screen.
Consistency and standards.
Users should not have to wonder whether different words, situations, or actions mean the same thing. Follow platform conventions.
Again, the word 'Begin Route' could cause confusion, but renaming the button to 'Start Shopping' would clarify to old people that start shopping is exactly that.
Predictive word like Open Office where if the user types in C, then all the ingredients listed that begin with C appear and it carries on filtering with every key press so that way the user can then select from the final 10 in the list or something of that type of UI.
Error prevention.
Even better than good error messages is a careful design which prevents a problem from occurring in the first place. Either eliminate error-prone conditions or check for them and present users with a confirmation option before they commit to the action.
The final screen shows that before the user is about to pay it does have a confirmation screen that allows them to confirm the price of what they have just bought.
Recognition rather than recall.
Minimize the user's memory load by making objects, actions, and options visible. The user should not have to remember information from one part of the dialogue to another. Instructions for use of the system should be visible or easily retrievable whenever appropriate.
As everything is on screen the user has all of the information to hand which means that they don't have to remember anything.
Flexibility and efficiency of use Accelerators
Unseen by the novice user -- may often speed up the interaction for the expert user such that the system can cater to both inexperienced and experienced users. Allow users to tailor frequent actions.
The more experience the user gets the more they will learn that they can add to their shopping list favourites to save them having to re-enter data into the system. Thanks to the store card the device can also monitor what items the person usually buys and asks them if they would like to add it to the shopping list.
Aesthetic and minimalist design
Dialogues should not contain information which is irrelevant or rarely needed. Every extra unit of information in a dialogue competes with the relevant units of information and diminishes their relative visibility.
The page that confirms the user is not needed, at this point anyone that has stolen a card and knows the pin number is going to confirm the person. The help button on the user confirmation page is not needed, however a help button on the login pages would be more helpful.
Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors
Error messages should be expressed in plain language (no codes), precisely indicate the problem, and constructively suggest a solution.
If the store card is inserted incorrectly then the device should display some sort of message
Help and documentation
Even though it is better if the system can be used without documentation, it may be necessary to provide help and documentation. Any such information should be easy to search, focused on the user's task, list concrete steps to be carried out, and not be too large.
There is no help for the main screen, some interactive help to make the user take the neccessary steps to start the shopping experience, such as searching for an item before hitting 'Begin Route'.
Cognitive Walkthrough by Tony
I park up to the closest parking space available… saving me walking distance as I have troublesome knees. I enter the store and head straight for the brand new super duper trolley.
Task 1: Entering Store card into ShopNav device
The screen tells me to “Insert Card”, so I pull out my wallet and search out my store card. I look around for a split second, finding the place to insert the card, and put it into the device. The screen then informs me to “Enter PIN”, as I deal with a lot of cards, I change all my PIN numbers to the same number, so I don’t have any trouble remembering.
Positives• I like dealing with the Store Card and not with cash
Negatives• Another card that is clustering up my wallet• As I have to insert the card, I am worried I may forget to take it out when I leave the store
Task 2: Using the product search facility
My weekly diet consists of pizza, so it’s the first thing that I want to search for. The search button on the interface is very visible, and it then takes me to the search screen. I type in pizza, and a list of pizzas comes up, I select the 1 that I want and select the “add to shopping list” button, which consequently adds it to my personal shopping list. I also search for Tagliatelle Pasta, but I get a spelling mistake, and it does not come up… so I have to result in having to walk to the pasta section myself to find it.
Positives• I can search for a product without having to search up and down isles
Negatives• If I get a spelling mistake, my search doesn’t return results• Having to type long names of products is time consuming
Task 3: View Recommendations
After searching for pizza, there is an alternative products list displayed next to it, displaying recommendations of complementary products. I love this feature, as I am the sort of person that likes to experience new things, the recommendations offers me a whole new world of food choices that I never knew about.
Positives• Recommends complimentary foods that I never knew about.
Negatives• Sometimes it can be annoying clustering up the screen with lots of products I don’t want
Task 4: Navigate user around the store
After creating my shopping list, I select the “Confirm List” button, which then provides me with the most efficient route around the store. As an individual that finds it hard walking long distances due to my troublesome needs, I found this aspect of the device revolutionary. As I walked around, I did want to veer off sometimes just to see some offers that are down certain isles.
Positives• Saves a lot of time and walking up and down the supermarket and isles searching for my product
Negatives• Sometimes I like to walk down isles viewing something new, or any great new offers that are on
Task 5: Adding product to Trolley
Whilst following the ShopNav’s route around the supermarket, I pick up the product and place it into the trolley. The product gets automatically added to my purchase list on the device, and informs me of it, and displays the total cost of the shopping so far. I also add Coca Cola into the trolley, the device beeps, and inform me on the screen that high level of sugar content is not recommended for my high blood pressure. As a person that hasn’t taken care of himself over the years, I didn’t realise how much sugar was actually in coca cola.
Positives• Thinks its great that he can see a running total of the cost of all goods in my trolley• It’s fantastic the way the device informs me of the health issues that come with products. Its invaluable information that everybody should be educated on.
Negatives• As I am overweight, I am looking to reduce my fat content, but when I added sausages into the trolley, it didn’t highlight that fact. Maybe a system, where I could put in a maximum % of fat content, so the system could highlight the issue just as it did for the coca cola.
Task 6: Removing a product from the trolley
I subsequently remove the coca cola from the trolley, and put it back onto the shelf. The device informs me that the product has been removed from the purchase list and the running cost total is recalculated and the cost of the coke taken off.
Positives• Great that the system automatically deals with removing the product from the purchase list, so I don’t have worry about purchasing goods that I have taken out.
Task 7: Paying for shopping
After a long shop, the thing I hate most is waiting in a long shopping queue waiting to pay for my goods, also standing their waiting for the checkout person to process all my bank details and enter my PIN number. This automatic purchasing attribute is fantastic, as I walk over the RFID readers, a “Confirm Purchase” buttons pops up showing my total cost and the list of products, I press confirm and the cost is automatically billed to my bank. My shopping time has halved, and can look forward to the evening not worrying about my knees hurting as much.
Positives• I love the fact that I don’t have to wait in queues for longs times
Negatives• Not to sure about the reliability as I have never used this before. What if it charges me twice or the RFID readers fail?
Task 8: Paying for shopping by cash I walk over to the checkout and purchase my goods in the traditional way.
Positives• Tried and trusted
Negatives• Have to wait in long queues, and there’s nothing worse for my knees
Task 1: Entering Store card into ShopNav device
The screen tells me to “Insert Card”, so I pull out my wallet and search out my store card. I look around for a split second, finding the place to insert the card, and put it into the device. The screen then informs me to “Enter PIN”, as I deal with a lot of cards, I change all my PIN numbers to the same number, so I don’t have any trouble remembering.
Positives• I like dealing with the Store Card and not with cash
Negatives• Another card that is clustering up my wallet• As I have to insert the card, I am worried I may forget to take it out when I leave the store
Task 2: Using the product search facility
My weekly diet consists of pizza, so it’s the first thing that I want to search for. The search button on the interface is very visible, and it then takes me to the search screen. I type in pizza, and a list of pizzas comes up, I select the 1 that I want and select the “add to shopping list” button, which consequently adds it to my personal shopping list. I also search for Tagliatelle Pasta, but I get a spelling mistake, and it does not come up… so I have to result in having to walk to the pasta section myself to find it.
Positives• I can search for a product without having to search up and down isles
Negatives• If I get a spelling mistake, my search doesn’t return results• Having to type long names of products is time consuming
Task 3: View Recommendations
After searching for pizza, there is an alternative products list displayed next to it, displaying recommendations of complementary products. I love this feature, as I am the sort of person that likes to experience new things, the recommendations offers me a whole new world of food choices that I never knew about.
Positives• Recommends complimentary foods that I never knew about.
Negatives• Sometimes it can be annoying clustering up the screen with lots of products I don’t want
Task 4: Navigate user around the store
After creating my shopping list, I select the “Confirm List” button, which then provides me with the most efficient route around the store. As an individual that finds it hard walking long distances due to my troublesome needs, I found this aspect of the device revolutionary. As I walked around, I did want to veer off sometimes just to see some offers that are down certain isles.
Positives• Saves a lot of time and walking up and down the supermarket and isles searching for my product
Negatives• Sometimes I like to walk down isles viewing something new, or any great new offers that are on
Task 5: Adding product to Trolley
Whilst following the ShopNav’s route around the supermarket, I pick up the product and place it into the trolley. The product gets automatically added to my purchase list on the device, and informs me of it, and displays the total cost of the shopping so far. I also add Coca Cola into the trolley, the device beeps, and inform me on the screen that high level of sugar content is not recommended for my high blood pressure. As a person that hasn’t taken care of himself over the years, I didn’t realise how much sugar was actually in coca cola.
Positives• Thinks its great that he can see a running total of the cost of all goods in my trolley• It’s fantastic the way the device informs me of the health issues that come with products. Its invaluable information that everybody should be educated on.
Negatives• As I am overweight, I am looking to reduce my fat content, but when I added sausages into the trolley, it didn’t highlight that fact. Maybe a system, where I could put in a maximum % of fat content, so the system could highlight the issue just as it did for the coca cola.
Task 6: Removing a product from the trolley
I subsequently remove the coca cola from the trolley, and put it back onto the shelf. The device informs me that the product has been removed from the purchase list and the running cost total is recalculated and the cost of the coke taken off.
Positives• Great that the system automatically deals with removing the product from the purchase list, so I don’t have worry about purchasing goods that I have taken out.
Task 7: Paying for shopping
After a long shop, the thing I hate most is waiting in a long shopping queue waiting to pay for my goods, also standing their waiting for the checkout person to process all my bank details and enter my PIN number. This automatic purchasing attribute is fantastic, as I walk over the RFID readers, a “Confirm Purchase” buttons pops up showing my total cost and the list of products, I press confirm and the cost is automatically billed to my bank. My shopping time has halved, and can look forward to the evening not worrying about my knees hurting as much.
Positives• I love the fact that I don’t have to wait in queues for longs times
Negatives• Not to sure about the reliability as I have never used this before. What if it charges me twice or the RFID readers fail?
Task 8: Paying for shopping by cash I walk over to the checkout and purchase my goods in the traditional way.
Positives• Tried and trusted
Negatives• Have to wait in long queues, and there’s nothing worse for my knees
Tuesday, 13 March 2007
Cognitive Walkthough by Maureen

Despite it being a delicate, warm, spring day, Maureen insists on her coat as she leaves the house for the supermarket.
Having made her store card for the ShopNav during her previous visit with the assistance of a store employee, she’s now ready to give it a go.
She already feels a bit uncomfortable by breaking her old routine; having to collect the trolley from a new area of the store, but she’s willing to give it a go.
Having made her store card for the ShopNav during her previous visit with the assistance of a store employee, she’s now ready to give it a go.
She already feels a bit uncomfortable by breaking her old routine; having to collect the trolley from a new area of the store, but she’s willing to give it a go.
Task 1: Entering Store card into ShopNav device
“Swipe Card” reads on the computer screen of the ShopNav (or NavShop as Maureen remembers it). She swipes the card several times with the barcode facing the wrong way, however eventually proceeds to the next screen. It worked on her final attempt before she approached a store assistant – the only reply she got was “try again”.
“Enter Pin”. Knowing a strong memory isn’t the best of her qualities, she wrote the PIN code when she made her store card last week. In her purse, she retrieves the small slip of paper and carefully enters. A sigh of relief it worked!
Improvements
- Insert card instead of swiping
- Another solution for pin? Is it actually required?
“Swipe Card” reads on the computer screen of the ShopNav (or NavShop as Maureen remembers it). She swipes the card several times with the barcode facing the wrong way, however eventually proceeds to the next screen. It worked on her final attempt before she approached a store assistant – the only reply she got was “try again”.
“Enter Pin”. Knowing a strong memory isn’t the best of her qualities, she wrote the PIN code when she made her store card last week. In her purse, she retrieves the small slip of paper and carefully enters. A sigh of relief it worked!
Improvements
- Insert card instead of swiping
- Another solution for pin? Is it actually required?
Task 2: Using the product search facility
Maureen’s shopping list:
Milk - Bread - Baked Beans - Oranges - Murray Mints - Tomato Soup x2 cans - Eggs - Orange Squash -Teabags
The instructions on the screen clear and she knows what she must do. However typing is very time consuming and Maureen’s becomes a bit frustrated with her slow typing speed and having to stand in one spot for so long.
Selecting products on the whole is fine, however, there is some confusion where Maureen is unable to remember the exact name of the product. She’s always remembered and gone by the pictures and colours on the label.
Improvements
- Intelligent search
- Display photos of items
Task 3: View Recommendations
“Ahhh finally - Can I just get my food now?” She mumbles to the screen. Having clicked done in the shopping list, a recommendations list appears. Maureen is slightly shocked, and reads the screen intently. After reading a bit, Maureen is a bit confused and decides to ignore it all by pushing “Begin Route”.
Improvements
- Display where in the shopping process she is – what’s going to happen next
- Show on what basis the product recommendations are coming from
Task 4: Navigate user around the store
Very happy to be moving Maureen carefully follows the large arrows directing her to the appropriate aisles. She becomes a bit concerned about being put off track when she has to move around obstacles. However this concern is eliminated by the “distance to item” reading on the screen.
Task 5: Adding product to Trolley
Improvements
- Display where in the shopping process she is – what’s going to happen next
- Show on what basis the product recommendations are coming from
Task 4: Navigate user around the store
Very happy to be moving Maureen carefully follows the large arrows directing her to the appropriate aisles. She becomes a bit concerned about being put off track when she has to move around obstacles. However this concern is eliminated by the “distance to item” reading on the screen.
Task 5: Adding product to Trolley
She places a bottle of milk into the trolley… a beep… she immediately looks at the screen for any changes. “Ah, the milk has appeared on the side of my screen – How did that happen?”.
Improvements
- Explain when you place a item in the trolley the barcode is automatically read, perhaps show an animation
Task 6: Removing a product from the trolley
Walking away from the ‘Juice’s Aisle’, Maureen becomes aware of an offer on a bottle of squash that she would like to swap with the bottle currently in her trolley. Apprehensive to experiment with this new piece of technology, she decides to ignore the 10p saving.
Improvements
- As with Task 5 – show an animation of the correct action/how barcode reader works
Task 7/8: Paying for Shopping
A notification appears on the screen informing her she has all the items she entered at the start. An option to pay by “card” or “at the counter” appears. Instantaneously she pushes “at the counter” for she is not keen on credit cards.
She goes straight to the cashier and hands the total displayed on the screen. The cashier inspects the trolley and screen and helps Maureen pack her bags.
“Do you not trust me?” questions Maureen “Do you suspect me of not declaring all the items in my trolley?”
Improvements
Improvements
- Explain when you place a item in the trolley the barcode is automatically read, perhaps show an animation
Task 6: Removing a product from the trolley
Walking away from the ‘Juice’s Aisle’, Maureen becomes aware of an offer on a bottle of squash that she would like to swap with the bottle currently in her trolley. Apprehensive to experiment with this new piece of technology, she decides to ignore the 10p saving.
Improvements
- As with Task 5 – show an animation of the correct action/how barcode reader works
Task 7/8: Paying for Shopping
A notification appears on the screen informing her she has all the items she entered at the start. An option to pay by “card” or “at the counter” appears. Instantaneously she pushes “at the counter” for she is not keen on credit cards.
She goes straight to the cashier and hands the total displayed on the screen. The cashier inspects the trolley and screen and helps Maureen pack her bags.
“Do you not trust me?” questions Maureen “Do you suspect me of not declaring all the items in my trolley?”
Improvements
- Payment without the need of a cashier - being able to walk directly to packing counter
Cognitive Walkthrough by Major Singh

Tony will answer the following 3 questions when performing a cognitive walkthrough using the task analysis
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
After the cognitive walkthrough, Singh's criticisms were:
- No Punjabi language support
- Annoying recommendations repeating themselve eg. Whiskey prohibition!
- An onscreen guide is needed for entering store card
Task 1: Entering Store card into ShopNav device
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
The device screen informed me to insert store card into device.
The store card reader was visible, but I wasn’t sure on which way to enter the store card.
An onscreen guide to entering the card would be useful
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
I understand that the store card is reading my card and loading my details.
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
Yes, my card was rejected when I entered it the wrong way.
Task 2: Using the product search facility
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
The search button was very visible on the main screen
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
I understood as I entered my search, the system was looking for the boneless chicken breast meat I wanted
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I found it difficult to enter my product as my English is not brilliant; I want a Punjabi version!
Task 3: View Recommendations
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I am given a list of recommended foods depending on my medical conditions; I was recommended salt free peanuts after picking up KP Salty Nuts.
This ensured my blood pressure wouldn’t rise.
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
I understand the system is looking out for my best interests
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I am repeatedly told not to pick up any Whiskey! This is very annoying!
I want Whiskey and this phencaude computer can’t stop me!
Task 4: Navigate user around the store
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
This was a great feature, I’m get annoyed at walking round the store aimlessly and part time teenage workers not helping you find products.
The device navigates me around the store in a very efficient manor
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Yes, I simply follow the on screen directions
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I intentionally took a wrong turn and the system did not notice. However, there is a ‘Stop’ feature I could have used when I fancied taking a detour to the ‘MEAT’ aisle.
Task 5: Adding product to Trolley
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
This was a great surprise, I didn’t realise the trolley scanned products. As I put an Organic Chicken leg into the trolley, a price was displayed! Bruuahhh!!
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Yes, I realised the product was being scanned as it was dropped into the trolley
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
Yes, the product information was displayed as it was scanned.
Task 6: Removing a product from the trolley
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I accidentally put some Quorn into my trolley mistaking it for Meat! As I removed the fake meat, it was taken off my running total.
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Yes
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
Yes
Task 7: Paying for shopping
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I was aware that I could pay by store card, but I pay with hard cash only. I didn’t use this feature
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
NA
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
NA
Task 8: Paying for shopping by cash
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I went to checkout as usual, the cashier confirmed my shop and asked me to give it her the money. I paid for it.
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Sure
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I’m always right, don’t worry bout it
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
The device screen informed me to insert store card into device.
The store card reader was visible, but I wasn’t sure on which way to enter the store card.
An onscreen guide to entering the card would be useful
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
I understand that the store card is reading my card and loading my details.
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
Yes, my card was rejected when I entered it the wrong way.
Task 2: Using the product search facility
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
The search button was very visible on the main screen
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
I understood as I entered my search, the system was looking for the boneless chicken breast meat I wanted
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I found it difficult to enter my product as my English is not brilliant; I want a Punjabi version!
Task 3: View Recommendations
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I am given a list of recommended foods depending on my medical conditions; I was recommended salt free peanuts after picking up KP Salty Nuts.
This ensured my blood pressure wouldn’t rise.
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
I understand the system is looking out for my best interests
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I am repeatedly told not to pick up any Whiskey! This is very annoying!
I want Whiskey and this phencaude computer can’t stop me!
Task 4: Navigate user around the store
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
This was a great feature, I’m get annoyed at walking round the store aimlessly and part time teenage workers not helping you find products.
The device navigates me around the store in a very efficient manor
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Yes, I simply follow the on screen directions
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I intentionally took a wrong turn and the system did not notice. However, there is a ‘Stop’ feature I could have used when I fancied taking a detour to the ‘MEAT’ aisle.
Task 5: Adding product to Trolley
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
This was a great surprise, I didn’t realise the trolley scanned products. As I put an Organic Chicken leg into the trolley, a price was displayed! Bruuahhh!!
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Yes, I realised the product was being scanned as it was dropped into the trolley
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
Yes, the product information was displayed as it was scanned.
Task 6: Removing a product from the trolley
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I accidentally put some Quorn into my trolley mistaking it for Meat! As I removed the fake meat, it was taken off my running total.
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Yes
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
Yes
Task 7: Paying for shopping
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I was aware that I could pay by store card, but I pay with hard cash only. I didn’t use this feature
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
NA
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
NA
Task 8: Paying for shopping by cash
Q1: Is the correct action made evident to the user?
I went to checkout as usual, the cashier confirmed my shop and asked me to give it her the money. I paid for it.
Q2: Do I understand a device action description with what I am trying to do?
Sure
Q3: Do I know if I’ve made a right or a wrong choice?
I’m always right, don’t worry bout it
Wednesday, 7 March 2007
Cognitive Walkthrough and Task Analysis
Cognitive walkthroughs are performed at any stage of design using a prototype. This approach is intended especially to help understand the usability of a system for first-time users, that is, for users in an exploratory learning mode.
A cognitive walkthrough starts with a task analysis that specifies the sequence of steps or actions required by a user to accomplish a task, and the system responses to those actions. The designers and developers of the software then walkthrough the steps as a group, asking themselves a set of questions at each step.
Data is gathered during the walkthrough, and afterwards a report of potential issues is compiled. Finally the software is redesigned to address the issues identified.
I will blog our task analysis and then each of our personas can carry out a cognitive walkthrough.
A cognitive walkthrough starts with a task analysis that specifies the sequence of steps or actions required by a user to accomplish a task, and the system responses to those actions. The designers and developers of the software then walkthrough the steps as a group, asking themselves a set of questions at each step.
Data is gathered during the walkthrough, and afterwards a report of potential issues is compiled. Finally the software is redesigned to address the issues identified.
I will blog our task analysis and then each of our personas can carry out a cognitive walkthrough.
Tuesday, 6 March 2007
Prototype: ShopNav Store Card
The ShopNav store card will be attained by the elderly person by completing an application form. It will only be eligible for individuals aged over 60. This will not conflict with the standard store card the supermarket provides for its other users. The ShopNav store card will especially designed to be used with our device which is attached on the trolley.
Design of ShopNav store card:
The store card will be specifically designed for our device so no other type of card can be inserted - so for example a unique indent on the card.

Features of the ShopNav store card:
- Chip and Pin service
- Personal data
- Bank details
- Dietary requirements
- Medical conditions
- Shopping history
- Save favourites - repeat buys - therefore allows automatic reminders
Prototype: Supermarket RFID Service
Once the shopper has completed their shopping, if they have decided to pay via the STORE CARD SERVICE using our device mechanism, then all they need to do is walk past the RFID reader strips placed towards the exit. They will be asked to confirm the payment. Once confirmed the payment is taken by the server sensor placed in the supermarket which is connected to the RFID reader strips. 

Monday, 5 March 2007
Prototype: Trolley Design
Two companies that I think design products particularly well are Dyson and Apple.
Over the weekend I used… the vacuum! The “Dyson07 with Root8Cyclone™ technology”. Having cleaned my bedroom floor, (I never realised the carpet was a beige colour), I went to empty the vacuum – simply pull a trigger, a flap at the bottom of the container opens, and its empty – “no contact with dust”. And that’s what I liked: no need to wash hands after because “no contact with dust” – got the job done in seconds!
contact with dust” – got the job done in seconds!
And with Apple, it’s the simplicity. It just works, the design is clean and things you don’t have to worry about are hidden far away.
So with those 2 products in mind here’s the trolley design:

Over the weekend I used… the vacuum! The “Dyson07 with Root8Cyclone™ technology”. Having cleaned my bedroom floor, (I never realised the carpet was a beige colour), I went to empty the vacuum – simply pull a trigger, a flap at the bottom of the container opens, and its empty – “no contact with dust”. And that’s what I liked: no need to wash hands after because “no
 contact with dust” – got the job done in seconds!
contact with dust” – got the job done in seconds!And with Apple, it’s the simplicity. It just works, the design is clean and things you don’t have to worry about are hidden far away.
So with those 2 products in mind here’s the trolley design:

Prototype: Hardware Device
The device will be attached to the trolley. The actual design of the device will be similar to the picture below, its size will be bigger and there will be a touchscreen.

The touchscreen feature will be very similar to that of the kiosks placed in the Bullring shopping centre:


These are the blueprint measurememts of our device, it will be attached to the head of the trolley.


The touchscreen feature will be very similar to that of the kiosks placed in the Bullring shopping centre:


These are the blueprint measurememts of our device, it will be attached to the head of the trolley.

Prototype meeting for ShopNav
Prototype: Device Touchscreen Interface
Here are some very basic images of our menu interface (in the steps they should appear):



The menu is touchscreen, so it will be easy for old people to use.

A keyboard appears with simple functions when the user presses the "SEARCH" button on the previous screen.
 Once the person presses the "BEGIN ROUTE" button, the main menu becomes transparent and the direction giver appears in a stronger colour/formatting.
Once the person presses the "BEGIN ROUTE" button, the main menu becomes transparent and the direction giver appears in a stronger colour/formatting.
Once the person walks past through the sensored checkouts, this screen pops up with the final payment information. If the person changes there mind they can go back through the check out and press the also press "GO BACK ".

Use Case Model
Questionnaire Results: Shopping Habits of the Elderly
After creating a comprehensive questionnaire, we subsequently visited a local community centre, Onnely House in Harborne, for over 50 year olds. The questionnaire was disbanded between 5 community members, and the results formalised.

1. What is your age group?
Laachmann -> 70 - 80
Alfred -> 80 - 90
Margrett -> 80 - 90
Judy -> 70 - 80
Robert -> 60 - 70
2. What is your marital status?
Laachmann -> Widowed
Alfred -> Married
Margrett -> Married
Judy -> Widowed
Robert -> Divorced
3. How many people do you shop for?
Laachmann -> 5
Alfred -> 2
Margrett -> 2
Judy -> 0
Robert -> 1
4. Do you do your own shopping?
Laachmann -> Yes
Alfred -> Yes
Margrett -> Yes
Judy -> No
Robert -> Yes
5. How many times do you visit the supermarket?
Laachmann -> Once a week
Alfred -> Once a week
Margrett -> Once a week
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Once a week
6. How much do you spend on average on a supermarket trip?
Laachmann -> £30-40
Alfred -> £10-£20
Margrett -> £10-£20
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Below £10
7. What medical conditions do you suffer from?
Laachmann -> Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, Poor Eyesight
Alfred -> Arthritis, Glaucoma, High Blood Pressure
Margrett -> Asthma, Arthritis
Judy -> High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, Poor Eyesight
Robert -> Overweight, High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol
8. How do you travel to the supermarket?
Laachmann -> Car
Alfred -> Bus
Margrett -> Bus
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Bus
9. What technological items do you use?
Laachmann -> Computerised Massage Chair/Orthopaedic Bed, Diabetes sugar level tester
Alfred -> None
Margrett -> Digital Camera, Mobile Phone
Judy -> Mobile Phone
Robert -> Computer, Mobile Phone
10. Which of the following have you used?
Laachmann -> Remote Control, Computer Keyboard
Alfred -> Remote Control, Computer Keyboard
Margrett -> Remote Control, Computer Keyboard
Judy -> Remote Control, Touch Screen, Computer Keyboard
Robert -> Remote Control, Joy Stick, Computer Keyboard, Touch Screen
11. Do you own a supermarket store card?
Laachmann -> Yes
Alfred -> No
Margrett -> No
Judy -> No
Robert -> Yes
12. How do you pay for your shopping?
Laachmann -> Credit Card
Alfred -> Cash
Margrett -> Cash
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Credit Card
13. If you do not use a Debit or Credit card would you consider shopping?
Laachmann -> N/A
Alfred -> No – I don’t know, maybe, they’re too much hassle
Margrett -> No – Don’t trust those blasted cards
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> N/A
Summary of Findings:
The questionnaire session was very valuable; we attained some very helpful information from the potential users. We outlined that many elderly people that attended the centre live on their own or just as a couple, resulting in them having to do their own shopping. It came to light that the community centre offers computer literacy classes, and that many of the elderly people in the community centre have used a computer.
One of the main questions which was very emphasised by the elderly people was the medical conditions question, which highlighted the fact that many of them have health issues and poor eyesight, and it was an all round consensus that they all found it very difficult and time consuming sifting through certain products on a supermarket shelf ensuring certain aspects which are bad for there health, especially with their poor eyesight, most of them struggling to read the required information.
It was found that a couple of the elderly people did not use Credit or Debit cards, the reasons for this mainly fell under the extra hassle of depositing their pension into a bank, and also not trusting credit cards.

1. What is your age group?
Laachmann -> 70 - 80
Alfred -> 80 - 90
Margrett -> 80 - 90
Judy -> 70 - 80
Robert -> 60 - 70
2. What is your marital status?
Laachmann -> Widowed
Alfred -> Married
Margrett -> Married
Judy -> Widowed
Robert -> Divorced
3. How many people do you shop for?
Laachmann -> 5
Alfred -> 2
Margrett -> 2
Judy -> 0
Robert -> 1
4. Do you do your own shopping?
Laachmann -> Yes
Alfred -> Yes
Margrett -> Yes
Judy -> No
Robert -> Yes
5. How many times do you visit the supermarket?
Laachmann -> Once a week
Alfred -> Once a week
Margrett -> Once a week
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Once a week
6. How much do you spend on average on a supermarket trip?
Laachmann -> £30-40
Alfred -> £10-£20
Margrett -> £10-£20
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Below £10
7. What medical conditions do you suffer from?
Laachmann -> Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, Poor Eyesight
Alfred -> Arthritis, Glaucoma, High Blood Pressure
Margrett -> Asthma, Arthritis
Judy -> High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, Poor Eyesight
Robert -> Overweight, High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol
8. How do you travel to the supermarket?
Laachmann -> Car
Alfred -> Bus
Margrett -> Bus
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Bus
9. What technological items do you use?
Laachmann -> Computerised Massage Chair/Orthopaedic Bed, Diabetes sugar level tester
Alfred -> None
Margrett -> Digital Camera, Mobile Phone
Judy -> Mobile Phone
Robert -> Computer, Mobile Phone
10. Which of the following have you used?
Laachmann -> Remote Control, Computer Keyboard
Alfred -> Remote Control, Computer Keyboard
Margrett -> Remote Control, Computer Keyboard
Judy -> Remote Control, Touch Screen, Computer Keyboard
Robert -> Remote Control, Joy Stick, Computer Keyboard, Touch Screen
11. Do you own a supermarket store card?
Laachmann -> Yes
Alfred -> No
Margrett -> No
Judy -> No
Robert -> Yes
12. How do you pay for your shopping?
Laachmann -> Credit Card
Alfred -> Cash
Margrett -> Cash
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> Credit Card
13. If you do not use a Debit or Credit card would you consider shopping?
Laachmann -> N/A
Alfred -> No – I don’t know, maybe, they’re too much hassle
Margrett -> No – Don’t trust those blasted cards
Judy -> N/A
Robert -> N/A
Summary of Findings:
The questionnaire session was very valuable; we attained some very helpful information from the potential users. We outlined that many elderly people that attended the centre live on their own or just as a couple, resulting in them having to do their own shopping. It came to light that the community centre offers computer literacy classes, and that many of the elderly people in the community centre have used a computer.
One of the main questions which was very emphasised by the elderly people was the medical conditions question, which highlighted the fact that many of them have health issues and poor eyesight, and it was an all round consensus that they all found it very difficult and time consuming sifting through certain products on a supermarket shelf ensuring certain aspects which are bad for there health, especially with their poor eyesight, most of them struggling to read the required information.
It was found that a couple of the elderly people did not use Credit or Debit cards, the reasons for this mainly fell under the extra hassle of depositing their pension into a bank, and also not trusting credit cards.
ShopNav Questionnaire
Thursday, 1 March 2007
Questionnaires
Questionnaires are an easy way for us to gather data from our target users.
We will use the following steps to design the questionnaire:
We will use the following steps to design the questionnaire:
- Defining the Objectives of the survey
- Determining the Sampling Group
- Writing the Questionnaire
- Administering the Questionnaire
- Interpretation of the Results
- Clarity
- No leading questions
- Avoid embarrassing questions
- Avoid hypothetical questions
Tuesday, 27 February 2007
Scenarios: Shopping for Goods with Major Singh

Carroll (2000) states that scenarios are a great usability assessment tool to support the design of a system. This subsequent blog outlines a hypothetical scenario of a user interacting with the trolley device in its intended Supermarket environment.
In the UK there are 4 main supermarket stores, Tescos, Asda, Sainsburys and Morrisons. All 4 have a similar layout consisting of isles, deli counters and checkouts. Isles are designed to grant shoppers enough space to ensure a smooth shopping experience, but at busy times isles can become congested with shoppers and out of control trolleys.
Major Singh’s – A typical Shopping Scenario
Major Singh walks into the supermarket, his back arched slightly forward and walking with a limp, his knees momentarily buckling under the weight of his giant torso….. the ex army veterans body has taken its toll, especially after his well publicised ‘torturing’ incident that occurred in the late 70s by militant group lead by the notorious Jack Baber from Major Singh’s time in the Indian army. Being an old fashioned independent person, Major does his own weekly shopping without fail.
It’s a Sunday, and Major Singh is doing his weekly shop, the supermarket it busy, the hustle and bustle of the supermarket reminds Major Singh of Jalandur, his home town back in India, a woman shoots past in a traditional metal trolley, Major Singh can hear those ominous beeps from the checkout…. he looks round, and sees the checkouts full to the brim with people purchasing their goods…. Major Singh mutters to himself “hai hai, pend di yaaar”, he wipes his face, winds up his moustache and goes and gets his new computerised shopping trolley.
Major Singh then prepares to add his shopping list to the trolley device via the user friendly simplistically intuitive computerised touch screen pad on the trolley. Major Singh is standing stationary in the middle of the entrance entering his shopping list, as people brush past him to get into the store…. if only there was a small area where he could spend 5 minutes declaring his shopping list. Major Singh swipes the trolley device with his personal shopping card which stores all of his medical conditions, dietary requirements and shopping patterns.
Major Singh adds the essentials into his shopping list; he uses the interface to add bread, milk, meat and whiskey. The device then computes a complex algorithm and provides major Singh with the most efficient route round the supermarket to collect his desired products. This saves Major Singh a lot of time, hassle and reduces the stress on his body instead of walking back and forth down isles.
As Major Singh goes, as Dale would say, “wild in the isles”, following the route provided to him by the trolley, he picks up his bottle of whiskey and places it into his trolley. The computerised device starts to flash and shows a warning message to Major Singh, it explains that the high levels of sugar content in the Whiskey is not suitable for Major Singh as he suffers from Type 2 diabetes. Major Singh subsequently removes the bottle out of the trolley and replaces it back onto the shelf; the product is automatically taken off the products list on the device.
In the UK there are 4 main supermarket stores, Tescos, Asda, Sainsburys and Morrisons. All 4 have a similar layout consisting of isles, deli counters and checkouts. Isles are designed to grant shoppers enough space to ensure a smooth shopping experience, but at busy times isles can become congested with shoppers and out of control trolleys.
Major Singh’s – A typical Shopping Scenario
Major Singh walks into the supermarket, his back arched slightly forward and walking with a limp, his knees momentarily buckling under the weight of his giant torso….. the ex army veterans body has taken its toll, especially after his well publicised ‘torturing’ incident that occurred in the late 70s by militant group lead by the notorious Jack Baber from Major Singh’s time in the Indian army. Being an old fashioned independent person, Major does his own weekly shopping without fail.
It’s a Sunday, and Major Singh is doing his weekly shop, the supermarket it busy, the hustle and bustle of the supermarket reminds Major Singh of Jalandur, his home town back in India, a woman shoots past in a traditional metal trolley, Major Singh can hear those ominous beeps from the checkout…. he looks round, and sees the checkouts full to the brim with people purchasing their goods…. Major Singh mutters to himself “hai hai, pend di yaaar”, he wipes his face, winds up his moustache and goes and gets his new computerised shopping trolley.
Major Singh then prepares to add his shopping list to the trolley device via the user friendly simplistically intuitive computerised touch screen pad on the trolley. Major Singh is standing stationary in the middle of the entrance entering his shopping list, as people brush past him to get into the store…. if only there was a small area where he could spend 5 minutes declaring his shopping list. Major Singh swipes the trolley device with his personal shopping card which stores all of his medical conditions, dietary requirements and shopping patterns.
Major Singh adds the essentials into his shopping list; he uses the interface to add bread, milk, meat and whiskey. The device then computes a complex algorithm and provides major Singh with the most efficient route round the supermarket to collect his desired products. This saves Major Singh a lot of time, hassle and reduces the stress on his body instead of walking back and forth down isles.
As Major Singh goes, as Dale would say, “wild in the isles”, following the route provided to him by the trolley, he picks up his bottle of whiskey and places it into his trolley. The computerised device starts to flash and shows a warning message to Major Singh, it explains that the high levels of sugar content in the Whiskey is not suitable for Major Singh as he suffers from Type 2 diabetes. Major Singh subsequently removes the bottle out of the trolley and replaces it back onto the shelf; the product is automatically taken off the products list on the device.
Monday, 26 February 2007
Scenarios: Purchasing Goods with Tony

The Scenario that I am going to explain is the user paying for all their goods. What I am going to demonstrate is:
- The type of environments that this system is usually used in.
- The technology that will be used
- The various processes that will happen to purchase items (see the image on the left)
- Why this is benificial to the target audience (old people)
The Types of Environments
Imagine a busy supermarket, your local Sainsbury's, Tesco's or Asda. Shoppers in every ilse rushing around buying their weekly shop. With some of the larger stores on average having 30 isles, shelving above head height stocked to the brim with goods, loads of busy shelf replenisment staff, and the worst is yet you come! You finally finish shopping for the week and you head of to the nearest check out to find the queue is like the M25.
The Technology that will be used
One of the latest pieces of technology to hit the market is RFID, RFID is a small silicon chip that can store information about items, so not great for databases but great for things that could be found at your local super market shelf, Mars Bars, Cheerios, Bread... etc...etc (for more information click here: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/6389581.stm ) So in essence you could store the bar code on this RFID chip and therefore remove the barcode, but then I can hear you say, why would you want to remove the bar code with this chips that cost more? Well simple, our idea encorparates the technological advances of RFID to remove the worst part of the shopping experience, the queing at the tills.
RFID readers are directional, which means that if we line the trolley with a couple of RFID readers facing intowards the trolley then any item that is put in the trolley can automatically be calculated removing the need for people having to queue to get their items paid for.
The Processes
In this example I will use one of our personas, Tony. So as Tony is doing his usual trip to his local Sainsbury's in his usual italian pin stripped shopping suit. He starts to throw in all the ingredients into his trolley that he needs for mama's secret recipe which he is planning on cooking later on tonight.
All the items that he has put into his trolley have RFID tags, so as he places them in his trolley the readers read the information of the item, and sends it to the trolley device which shows on screen the price and the nutrional information. Once Tony has finished his shopping trip he walks over the checkout and instead of tilling up he just walks past the tilling sensors that will automatically charge him through his store card. This means that he doesn't have to wait, it's like walking through an X-ray machine.
So... recapping quickly using bullet points:
- Tony adds an item to the trolley
- The trolley RFID readers pick up this new item, relays the information to the trolley device showing information on screen
- Tony finishes his shopping trip and walk through the tilling isle (without queuing)
- At this point the Trolley device has sent the information to the store charging/EPOS system that has taken the payment with the use of information of the store card that was placed into the trolley device.
Why is this Beneficial to Old People
Well as we know old people aren't the nimblest or quickest people in a supermarket. Firstly this technology means that - They don't have to worry about having to take the items out of the trolley
- Having to place items on the conveyor belt
- Bagging the items really quickly
- Hunting around for their card to pay for the goods
- Placing the bags back into the trolley.
Missing out these steps removes the need for physical strains for old people when shopping.
- The type of environments that this system is usually used in.
- The technology that will be used
- The various processes that will happen to purchase items (see the image on the left)
- Why this is benificial to the target audience (old people)
The Types of Environments
Imagine a busy supermarket, your local Sainsbury's, Tesco's or Asda. Shoppers in every ilse rushing around buying their weekly shop. With some of the larger stores on average having 30 isles, shelving above head height stocked to the brim with goods, loads of busy shelf replenisment staff, and the worst is yet you come! You finally finish shopping for the week and you head of to the nearest check out to find the queue is like the M25.
The Technology that will be used
One of the latest pieces of technology to hit the market is RFID, RFID is a small silicon chip that can store information about items, so not great for databases but great for things that could be found at your local super market shelf, Mars Bars, Cheerios, Bread... etc...etc (for more information click here: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/6389581.stm ) So in essence you could store the bar code on this RFID chip and therefore remove the barcode, but then I can hear you say, why would you want to remove the bar code with this chips that cost more? Well simple, our idea encorparates the technological advances of RFID to remove the worst part of the shopping experience, the queing at the tills.
RFID readers are directional, which means that if we line the trolley with a couple of RFID readers facing intowards the trolley then any item that is put in the trolley can automatically be calculated removing the need for people having to queue to get their items paid for.
The Processes
In this example I will use one of our personas, Tony. So as Tony is doing his usual trip to his local Sainsbury's in his usual italian pin stripped shopping suit. He starts to throw in all the ingredients into his trolley that he needs for mama's secret recipe which he is planning on cooking later on tonight.
All the items that he has put into his trolley have RFID tags, so as he places them in his trolley the readers read the information of the item, and sends it to the trolley device which shows on screen the price and the nutrional information. Once Tony has finished his shopping trip he walks over the checkout and instead of tilling up he just walks past the tilling sensors that will automatically charge him through his store card. This means that he doesn't have to wait, it's like walking through an X-ray machine.
So... recapping quickly using bullet points:
- Tony adds an item to the trolley
- The trolley RFID readers pick up this new item, relays the information to the trolley device showing information on screen
- Tony finishes his shopping trip and walk through the tilling isle (without queuing)
- At this point the Trolley device has sent the information to the store charging/EPOS system that has taken the payment with the use of information of the store card that was placed into the trolley device.
Why is this Beneficial to Old People
Well as we know old people aren't the nimblest or quickest people in a supermarket. Firstly this technology means that - They don't have to worry about having to take the items out of the trolley
- Having to place items on the conveyor belt
- Bagging the items really quickly
- Hunting around for their card to pay for the goods
- Placing the bags back into the trolley.
Missing out these steps removes the need for physical strains for old people when shopping.
Sunday, 25 February 2007
Paper Design and Interface of Device
Here is just a brief idea of what I think the device should look like. I will produce a clearer version in my next post when I finally get Visio. Its in the design process at the moment, I'll get the measurements etc in the next post.
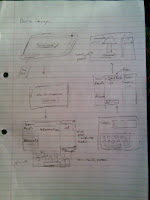 For a start I have designed the menus, here is a step by step approach in using the device menus:
For a start I have designed the menus, here is a step by step approach in using the device menus:
step 1 - there is start screen saying "Please Insert Store Card"
step 2 - once inserted the device displays the persons name from the store card and asks "Confirm" or "Cancel"
step 3 - once confirmed we have the main image right of us- it will also have the person name on there somewhere
the person name on there somewhere
step 4 - when the person wants to search, they touch the search button (touch screen) then a new menu pops up with a big simple keyboard on screen and the search field, the person types in whatever they look for and press return
step 5 - results are displayed and recommendations, then when the person clicks on a certain food, the info section changes accordingly - gives the price etc
step 6 - then they press the add button to add it to shopping list
step 7 - any updates/changes to shopping list will be noted by having different background colors depending on what was changed, so if new item added, it will highlight it green for a bit
step 8 - the person can press "begin route" then this produces an updated route and begins the direction giving - you might be thinking where are there directions on the screen? they will be at the forefront of the menu, making the back menu slightly transparent and giving a more stronger color to directions and instructions it provides - so imagine seeing a red arrow pointing forward and below it "6 meters"
step 9 - if the person see's another item they want on the shelf, they simply press stop on the screen and drop the item in the trolley, the rfid trolley readers scan the product and automatically add it to shopping list and total price....
step -10 the person can then press begin route again, which recalculates any changes and continues as step 8
step 11 - once the person has finsihed shopping, they can walk through the checkouts which will uatomatically ask the person to confirm the goods they have brought and the amount the have to pay, so "Pay" ->> "Confirm Amount" ->>>>"Thank you for shopping at ...."
step 12 - person then removes their shopping and leaves the trolley and device in-store
 For a start I have designed the menus, here is a step by step approach in using the device menus:
For a start I have designed the menus, here is a step by step approach in using the device menus:step 1 - there is start screen saying "Please Insert Store Card"
step 2 - once inserted the device displays the persons name from the store card and asks "Confirm" or "Cancel"
step 3 - once confirmed we have the main image right of us- it will also have
 the person name on there somewhere
the person name on there somewherestep 4 - when the person wants to search, they touch the search button (touch screen) then a new menu pops up with a big simple keyboard on screen and the search field, the person types in whatever they look for and press return
step 5 - results are displayed and recommendations, then when the person clicks on a certain food, the info section changes accordingly - gives the price etc
step 6 - then they press the add button to add it to shopping list
step 7 - any updates/changes to shopping list will be noted by having different background colors depending on what was changed, so if new item added, it will highlight it green for a bit
step 8 - the person can press "begin route" then this produces an updated route and begins the direction giving - you might be thinking where are there directions on the screen? they will be at the forefront of the menu, making the back menu slightly transparent and giving a more stronger color to directions and instructions it provides - so imagine seeing a red arrow pointing forward and below it "6 meters"
step 9 - if the person see's another item they want on the shelf, they simply press stop on the screen and drop the item in the trolley, the rfid trolley readers scan the product and automatically add it to shopping list and total price....
step -10 the person can then press begin route again, which recalculates any changes and continues as step 8
step 11 - once the person has finsihed shopping, they can walk through the checkouts which will uatomatically ask the person to confirm the goods they have brought and the amount the have to pay, so "Pay" ->> "Confirm Amount" ->>>>"Thank you for shopping at ...."
step 12 - person then removes their shopping and leaves the trolley and device in-store
Thursday, 22 February 2007
Modifications to our final Idea
After taking all the criticisms into account we decided to add and remove a few functionalities to our idea. This was all discussed in our team meeting yesterday.
We have decided to present our idea in a diagram so it is easier to digest.

Summary of key features
We have decided to present our idea in a diagram so it is easier to digest.

Summary of key features
- The recommendations device can be used to scan products and return a list of recommendations and recipes depending on user preferences and medical conditions.
- The device can also be used to search for products and the device will act like a 'Satnav' and guide the user around the store to these products in the most efficient way.
- The trolley will be very light because it will electrically powered making it easy to push
- A store card with personal details, bank details, medical conditions will be swiped into the device.
- The device will be linked to an online server which will carry out the transaction as the user drops the products into the trolley
Tuesday, 13 February 2007
Criticisms
 We have identifed the technology we would like to develop for the elderly.
We have identifed the technology we would like to develop for the elderly.However there are a few criticisms that we would like to to answer and modify our idea accordingly...
- Why not encourage the elderly to use online shopping?
- Moving the trolley outside? What if the person wants to get home on the bus?
- Would this trolley work in smaller supermarkets?
- When the trolley is moving by itself, it limits the amount of freedom the user has.
For example, the user might make an impulse purchase, as he/she picks up a product the trolley may have disappeared into the distance..
Our view to these criticisms...
- We all know of the growing popularity of online shopping, however a lot of people are still are hesitant to provide credit card details due to security scares.
Furthermore, we recognised in our brainstorms that elderly people like to remain independent. Online shopping does not allow this. Our technology would allow the elderly to shop for themselves - After careful thought and deliberation we have decided to remove the 'Trolley outside' feature from our idea.
We have removed this idea because the scope of the initial idea was too wide and we would like to concentrate on the functionality inside the store. - The supermarkets will decide whether the trolley is applicable in their branch.
- After analysing automatic trolley feature we have decided to implement a motored engine that powers the trolley. This means that the elderly person will only need to push the trolley slightly and the engine will power the wheels.
This technology has already been implemented in electronic pallet trucks in cash and carries.
(http://www.howardhandling.co.uk/products.php?PageId=4)
Electronic pallet trucks are very expensive, the average cost being £1800 for 1400kilos. Obviously we don't need such a high capacity - the trolley will need to handle 20kg max.
Final Idea: The Ultimate Shopping Experience
After our meating earlier on today, we decided on our final idea:
We have come to a consensus that we should concatenate two of our most prominent ideas:
The Supermarket recipe advisor and The Motion Sensor Trolley
(Please see the previous posts to why the elderly would find these technologies useful)
By merging these ideas, our technology will offer the ultimate shopping experience for elderly people. The issues our technology will deal with is the difficulties elderly people suffer from when shopping, which are:
Supermarkets today are a mess.
"I went into Safebury's, I took a look around and realised that God left this place a long time ago" - Biling Di Caprio
I couldn't be more pleased with this idea
We have come to a consensus that we should concatenate two of our most prominent ideas:
The Supermarket recipe advisor and The Motion Sensor Trolley
(Please see the previous posts to why the elderly would find these technologies useful)
By merging these ideas, our technology will offer the ultimate shopping experience for elderly people. The issues our technology will deal with is the difficulties elderly people suffer from when shopping, which are:
- Walking around the supermarket during busy times,
- Forgetting shopping lists (Poor memory)
- They find it difficult to find items for diets that are dictated by illnesses/medical conditions
- Getting lost in the shop
- Having to walk back and forth around the store for multiple items (Inefficient)
- People with poor eyesight are unable to read products and ingredients
- Elderly people get tired when waiting in long queues
- Supermarket recipe advisor - a device that will recommend recipes depending on what product is scanned into the device. The device will recommend products depending on:
- Persons health issues
- Recommend certain foods depending on medical conditions. eg Cod liver oil for arthritis
- All of the users information will be on the persons store card. eg. Health information, Shopping habits
- The device will have a budget advisor and offer cheaper products - good for penny saving pensioners.
- This device will be detachable from the trolley
- Motion Sensor Trolley - The trolley will have two functions, inside the store and outside.
- Inside the Store -
- The trolley will automatically navigate the person around the store depending on their shopping. This could be done using a Dijkstras algorithm which calculates the shortest route.
- The trolley will navigate the user depending on the type of products the recipe advisor/shopping lists includes.
- For example, If the user wanted to purchase Milk and Bananas, the trolley will guide the user to the Milk first because it is a heavier product. We will implement this because if Bananas were put in the trolley first, they would be damaged by heavier items such as Milk bottles.
- The trolley will have motion sensors to ensure it does not collide with anything in the store. eg. People, Shelves, Other trolleys etc. This could be done using 'Collision Theory'
- There will be a pause/stop button on the trolley. This can be used if the person finds an item that is not on the shopping list and wants to add it to the trolley.
- Outside the Store -
- The trolley will be controlled by motion sensors installed in the users shoes.
- We will NOT implement the supermarket sensors in the outside environment because there are an unlimited amount of obstacles.
- The trolley will be designed to deal with the external environment. For example:
- Durable wheels
- Active suspension and hydraulics to deal with pavements
- A trolley cover to protect the shopping from rain
- Intelligent Store Card
- Along with user information, the card will have bank/debit details. It will connect to an online server that deals with the transactions.
- This will eliminate the need for waiting in queues
- The recipe advisor device screen will have a running total of costs
- The trolley will scan the product prices as it is dropped into the trolley
- When an item is taken out, it will be taken off the shopping list
- The final payment will be made once the user walks out of the supermarket, a sensor will automatically take a payment for the shopping.
Supermarkets today are a mess.
"I went into Safebury's, I took a look around and realised that God left this place a long time ago" - Biling Di Caprio
I couldn't be more pleased with this idea
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




















